Water covers about 71% of the Earth's surface, mostly in seas and oceans (about 96.5%).Water is one of the world’s most precious resources. It connects us all and is essential to everything we do. Water is also vital for agriculture, livestock and fisheries and key to food production, nutritional security and health.
Water is fundamental to photosynthesis and respiration. Photosynthetic cells use the sun's energy to split off water's hydrogen from oxygen.

Water plays an important role in the world economy. Approximately 70% of the freshwater used by humans goes to agriculture. Fishing in salt and fresh water bodies is a major source of food for many parts of the world, providing 6.5% of global protein.
Water is an excellent solvent for a wide variety of substances both mineral and organic; as such it is widely used in industrial processes, and in cooking and washing.
Pure water is visibly blue due to absorption of light in the region ca. 600 nm – 800 nm. The color can be easily observed in a glass of tap-water placed against a pure white background, in daylight.
According to FAO’s latest report on the State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture-global water quality is deteriorating at an alarming rate, and land and water resources around the world are at a breaking point.
Globally, about 80 percent of wastewater is discharged into the environment without adequate treatment, and one third of all rivers, deltas and tributaries in Latin America, Africa and Asia are severely polluted with pathogens, putting the health of millions of people at risk.
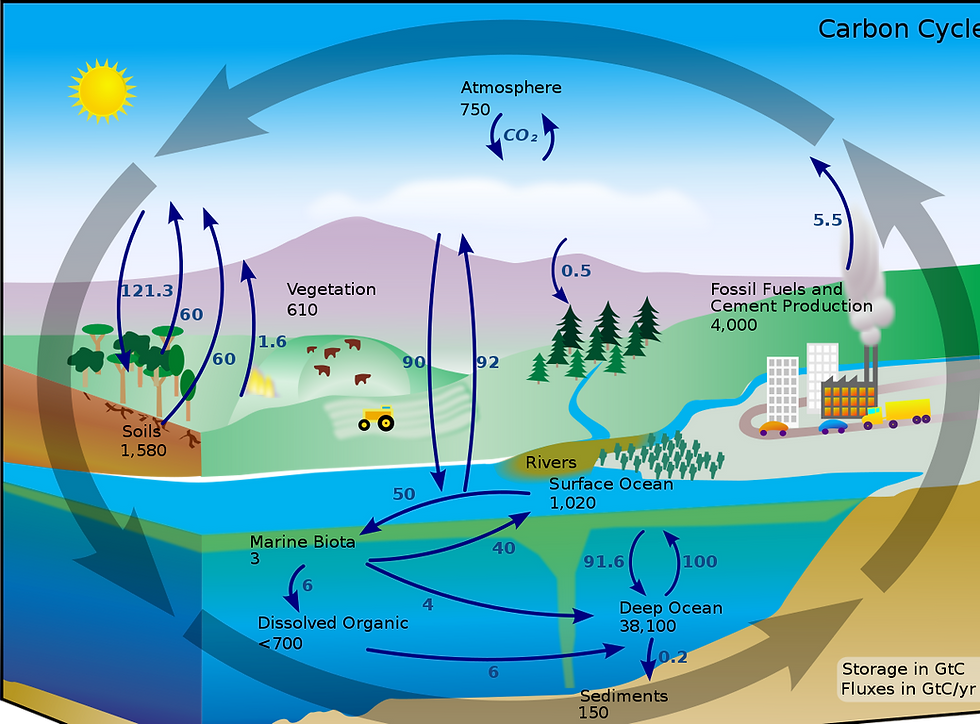
Involvement of water cycle plays a main role in deterioration of water present in both ground and underground water . Water cycle-The water cycle (known scientifically as the hydrologic cycle) refers to the continuous exchange of water within the hydrosphere, between the atmosphere, soil water, surface water, groundwater, and plants.
Quality of water -play a key role in whack of Food quality and it is an important aspect to manage throughout the entire supply chain, from production to consumption. Foodborne illnesses are often a result of consuming food contaminated from poor-quality water.
Managing water quality in the context of food safety will reduce the exposure to harmful pathogens in water and the resultant food supply.
Water fit for human consumption is called drinking water or potable water. Water that are not fit for human consumption are called non-potable water ,this can be reused by using various methods i.e., distillation or filtration .
By incorporating water quality into food safety considerations and applying genomic surveillance to this process, the program is enabling countries to address water and food quality as an integrated issue.
Water reclamation is the process of converting wastewater (most commonly sewage, also called municipal wastewater) into water that can be reused for other purposes . This process commonly used in countries like Japan.
In developing countries, 90% of all municipal wastewater still goes untreated into local rivers and streams. This affects both the Aquatic and Non-Aquatic Life forms by dumping the waste and making it into polluted water .
GOVT/ORGANISATION :
Currently, FAO is running a pilot in six countries where using WGS for surveillance of pathogens from water to food has never been done. As one example, FAO is working with Indonesia’s National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN) to implement a genomic study on water quality in chicken-fish farming systems in Blitar , East Java. A common practice in this area, integrated chicken-fish farming involves raising chickens alongside fish. Connecting these systems allows the manure from chickens to fertilize pond water and generate food for fish. Manure is a very efficient fertilizer, generating phytoplankton and zooplankton growth that fish then eat.
Innovative WGS technology provides rapid identification and characterization of microorganisms with a level of precision not previously possible.
Prevention is the best strategy. For this, we must ensure that knowledge of pre-harvest factors in food safety, particularly regarding water quality, is built into food production globally. This is particularly crucial as global water scarcity pushes us towards the use of poor-quality water sources. Better understanding of the connections between water quality and food safety is needed to safeguard human health, implement sustainable agriculture and improve environmental outcomes.
source: FAO
BY KHAS
.jpeg)

Comments